The Everlasting Shoe: What Does a 5,500-Year-Old Shoe Discovered in a Cave Tell Us About Ancient Armenians?
As any archaeologist knows, very few things other than stone last for a long time. In a moist, warm climate, most organic material such as hemp, cloth, wood, and leather will decay, leaving nothing but stone and perhaps bone at an archaeological site.
This is one reason why the Stone Age got its name, not because everything was made of stone, but because it is mostly stone tools and ornaments that have survived and thus it is mainly stone items that are representative of that time-period.
All organic materials such animal skins worn by Paleolithic or Neolithic peoples have, for the most part, disappeared. In the right environment though, such materials can last for thousands of years.
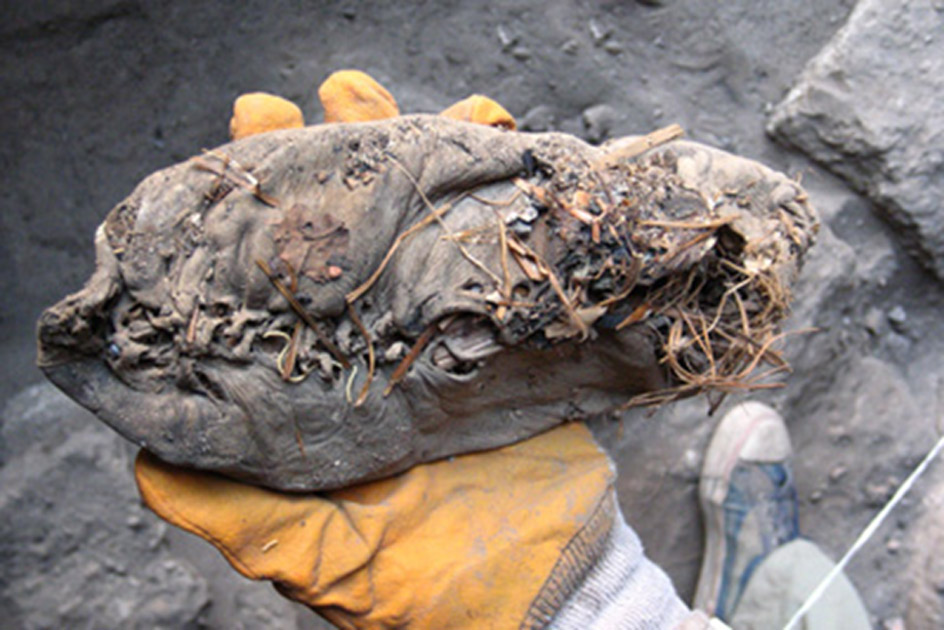
If an environment is dry, and undisturbed, normally fragile, perishable material can last for millennia. One example of this is a 5,500-year-old leather shoe found in an Armenian cave which is one of several other examples of ancient footwear.

Other Preserved Ancient Shoes
Two other famous examples of ancient footwear are sandals found in the Arnold Research Cave in Missouri and another in the Cave of the Warrior in the Judaean Desert.
The shoes in the Arnold Research Cave are between 800 and 8,000 years old. The youngest were made of deerskin while the oldest were sandals made of fibers from a plant called rattlesnake master.
The shoes found in the Cave of the Warrior were also sandals made from leather that were determined to be about 6,000 years old. The leather sandals were found with a reed mat, a bow with a quiver of arrows, and a flint knife, among other items.
The Judaean Desert is known for its dry climate, providing excellent preserving conditions. The desert has also been used for thousands of years by fugitives on the run who hid their belongings in caves and never retrieved them.
Other items found in the Judaean Desert include the Dead Sea Scrolls dating to between 200 BC and 200 AD and a cache of bronze instruments and ornaments determined to be about 6,000 years old.

It should be noted that the two other examples of ancient footwear were not directly dated, but were dated using comparison with other artifacts found in the caves.
The Armenian shoes were directly dated with radiocarbon dating. The great antiquity of the Armenian shoe is thus more certain than the antiquity of the other shoes.
The Armenian Shoe
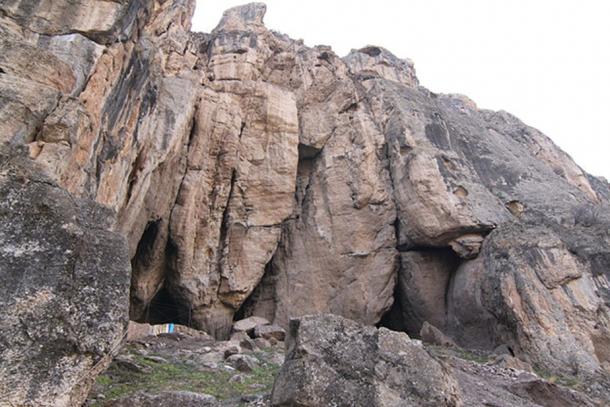
The 5,500-year-old shoe was discovered by an Armenian graduate student from the Institute of Archaeology of Armenia, Diana Zandaryan. The shoe was preserved by both the cold, dry conditions of the cave and a layer of sheep dung which was covering it, acting as a weathering seal.
Along with the shoe, containers of wheat, barley, and apricots were also discovered. The shoe dates to about 3,500 BC making it is a few centuries older than the initial levels of Stonehenge, the construction of which began in 3,000 BC.
It is not certain why the shoe or the other items were left there. They could have been left for storage or hidden there in a time of conflict. It is also possible that they were left there as an offering, possibly of a religious nature.
Another question is whether it was worn by a man or a woman. The shoe is small, women’s size by modern European and American standards, however it could have also been worn by a man in this time-period.
Life and Times of the Shoe
During the time that this shoe was in use, the inhabitants of Armenia had already been farming for thousands of years, having adopted domesticates from the Levant.
It is also around this time that the Kurgan culture, the proposed carriers of the Proto-Indo-European language began to move out of their ancestral homeland.
Little is known about the Kurgan culture except that they buried their dead in large mounds referred to as kurgans. These mounds are the most archaeologically visible features that they left behind, hence the name of the culture.
It is unknown whether the inhabitants of the caves were in some way related to the Kurgan culture, but we do know interesting things about them.
The people of Armenia of this day used domesticates prevalent during the Neolithic, including wheat, barley and sheep. Armenia was one of the earliest regions to adopt farming and pastoralism.
The archaeological site of Aratashen, which was inhabited about 8,000 years ago, has shown many details of the Neolithic culture of Armenia. They lived in adobe houses, raised barley and had shovels, spoons, and other tools made from wood, bone, and obsidian.
These shoes reveal yet another facet of Prehistoric Armenia, which is already known for its relatively rich archaeological record.
Eventually with enough research, we may learn more things about their culture beyond just what type of shoes they wore, what they ate and other aspects of their material culture.
We may also learn about the immaterial aspects of their culture, such as small glimpses of how they viewed the world.



















