Archaeologists Find 300,000-Year-Old Elephant Skeleton in Germany
According to recent findings, archeologists have discovered the nearly complete skeleton of a massive and now extinct elephant that lived in what is now the northern German city of Schöningen about 300,000 years ago.
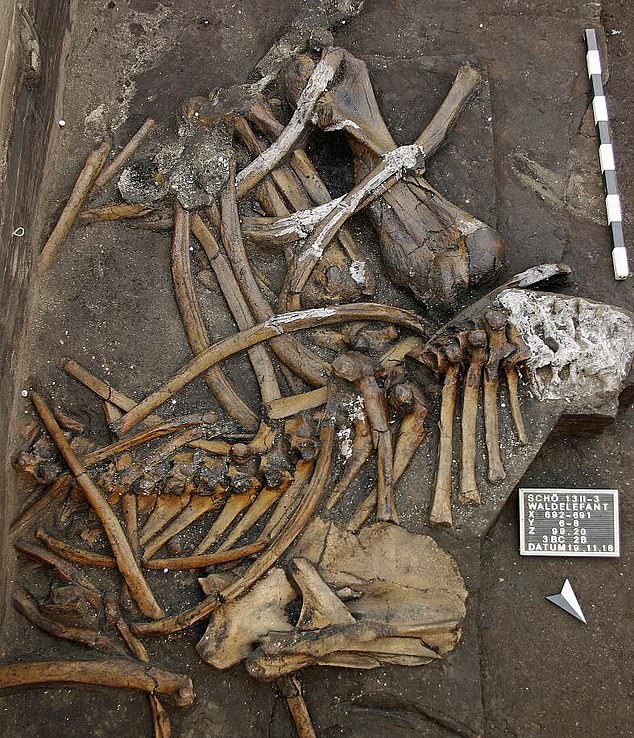
While this elephant – the straight tusked Eurasian elephant (Palaeo-loxodon antiquus) – presumably died of old age, meat eaters immediately consumed it; bite marks in the bones of this elephant show carnivores feasting on the dead animal, and bones and flint flakes found close to the elephant mean that people scavenged everything left, the researchers said.
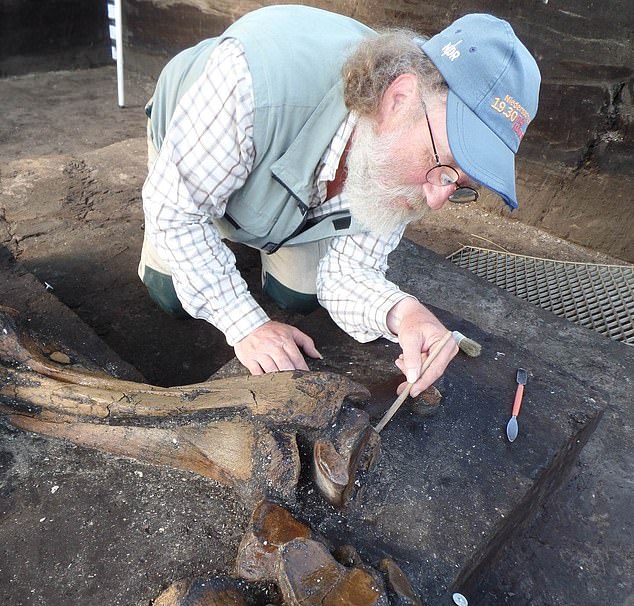
“The Stone Age hunters probably cut meat, tendons and fat from the carcass,” project researcher Jordi Serangeli, head of the excavation in Schöningen, said in a statement. The elephant died on the western side of a vast lake, a hint that it perished from natural causes.

Ivo Verheijen, a Doctoral student of Archaeozoology and Paleontology at the University of Tübingen, said that “elephants always stay nearby and in the water while they are sick or aged.”In addition, the elephant, a female, had worn teeth, suggesting it was old when it died, he said.
Researchers have found the remains of at least 10 elephants dating to the Lower Paleolithic-also known as the Old Stone Age(about 3 million to 300,000 years ago)-over the past several years at Schöningen.
But this new find is by far the most complete. The remains include 7.5-foot-long (2.3 meters) tusks – which are 125% longer than the average 6-foot-long (1.8 m) tusk of a modern African elephant, according to Encyclopedia Britannica.
The researchers also found the complete lower jaw, numerous vertebrae and ribs, large bones from three of its four legs and all five of its delicate hyoid bones, which are found in the neck and help support the tongue and voice box.
This P. antiquus elephant had a shoulder height of about 10.5 feet (3.2 m) and would have weighed about 7.5 tons (6.8 metric tons). “It was therefore larger than today’s African elephant cows,” Verheijen said.
Near these remains, researchers found 30 small flint flakes and two long bone tools. Micro flakes embedded in these two bones suggests the ancient humans who scavenged the elephant used them to sharpen stone tools (called knapping) at the site, said project researcher Bárbara Rodríguez Álvarez, an archaeologist at the University of Tübingen.
Of note, the ancient humans who likely scavenged the elephant were not Homo sapiens. The earliest evidence of H. sapiens in Europe dates to about 45,000 years ago, according to excavations at a cave in Bulgaria, a study published few month ago in the journal Nature Ecology and Evolution found.
Instead, these human scavengers were likely H. heidelbergensis, an extinct human relative who lived about 700,000 to 200,000 years ago, the researchers in Germany said.
Wildlife watering hole
The lake was a popular hole for elephants, according to several of their preserved footprints just 330 feet (100 m) from the new elephant excavation site.
“It must have been a small bunch of adults and younger animals,” said Flavio Altamura in the statement, a researcher at the Department of Antiquity at Sapienza University in Rome. “The big creatures marched around the lakeshore and their footprints sunk into the water , leaving triangular tracks behind.”
These elephants would have lived in a comfortable climate, compar-able to today’s; about 300,000 years ago, Europe was in the Reinsdorf interglacial, a warmer period bookended by two glacial (or colder) periods. Other animals thrived there, too.
About 20 kinds of large animals lived around the lake, including lions, bears, saber-toothed cats, rhinoceroses, wild horses, deer and large cattle, according to excavations. “The wealth of wildlife was similar to that of modern Africa,” Serangeli said.
All of these animals attracted ancient human hunters. Archaeologists have found the remains of 10 wooden spears and one throwing stick from 300,000 years ago, according to a study published online April 20 in the journal Nature Ecology and Evolution.

The new finding was uncovered in a collaborative effort between the Senckenberg Centre for Human Evolution and Palaeoenvironment at the University of Tübingen in Germany and the Lower Saxony State Office for Heritage. The research had published in the magazine “Archäologie in Deutschland” (Archaeology in Germany) and was presented at a press conference in Schöningen on May .


